Overview
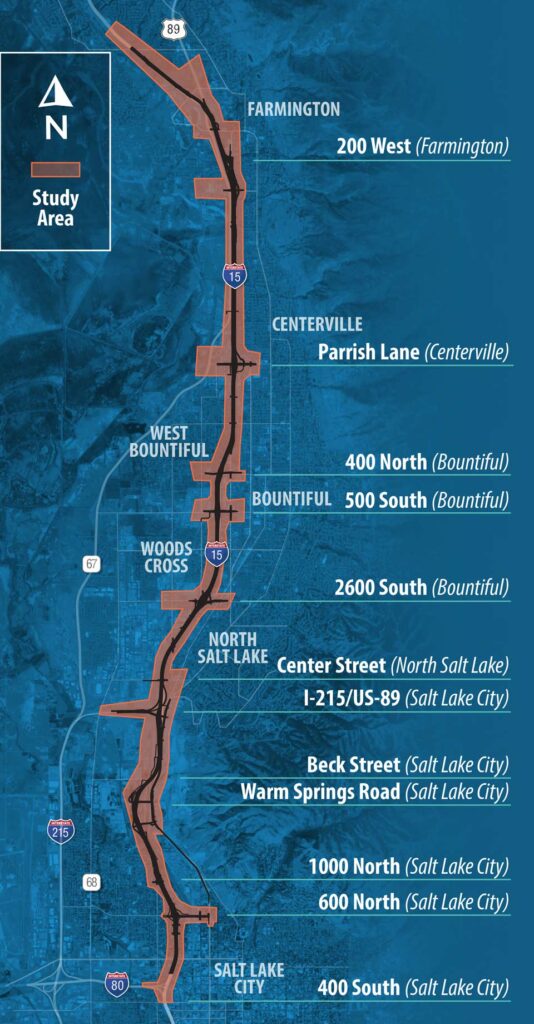
As part of its mission to improve quality of life through transportation, the Utah Department of Transportation (UDOT) has conducted an environmental study along the I-15 corridor between Farmington and Salt Lake City to identify solutions to transportation challenges through the year 2050.
Based on public feedback during the Alternatives Development Phase in Winter 2022-2023 and additional technical evaluation, the study team prepared a Draft Environmental Impact Statement (DEIS) for public review and comment. That public comment period ended Nov. 13, 2023. The study team has now released the Final Environmental Impact Statement (FEIS) and the accompanying Record of Decision (ROD). The below Final EIS and Record of Decision reflect the input of stakeholders throughout the study process that balance impacts with needed outcomes.
If you have any questions please contact the study team.
Final Environmental Impact Statement and Record of Decision
The Final EIS contains the information about the purpose and need for a project in the study area, technical analysis of various alternatives, description of the preferred alternative, potential impacts and mitigations associated with the preferred alternative, and a record of public engagement conducted and feedback received during the process. We invited the public to review these materials and provide feedback on the Draft EIS during the comment period from Sept. 29 to Nov. 13, 2023.
Navigating the Report
The FEIS Executive Summary and Record of Decision PDFs below contain a brief background about the study purpose, processes and contents. The following chapters and appendices provide more detailed information.
Cover Sheet and Contents
Chapter 1 – Purpose and Need
Chapter 1 – Purpose and Need – English (PDF)
Chapter 1 – Purpose and Need – Español (PDF)
Chapter 2 – Alternatives
Chapter 2 – Alternatives – English (PDF)
Chapter 2 – Alternatives – Español (PDF)
Chapter 3 – Affected Environment, Impacts, and Mitigation
Chapter 3 (part one)
Includes Land Use, Social Environment, Right-of-way and Relocations, Environmental Justice Populations, Economic Conditions, Transportation and Mobility, Joint Development, Air Quality, Noise, Historic and Archaeological Resources, and Water Quality and Water Resources impacts.
Chapter 3 – part one – English (PDF)
Chapter 3 – part one – Español (PDF)
Chapter 3 ( part two)
Includes Ecosystem Resources, Floodplains, Hazardous Materials and Hazardous Waste Sites, Visual Resources, Energy, and Construction Impacts, as well as the Indirect and Cumulative Effects, Short-term Uses versus Long-term Productivity, Irreversible and Irretrievable Commitment of Resources, Permits, Reviews, Clearances and Approvals, Mitigation, the Mitigation Summary and References.
Chapter 3 – part two – English (PDF)
Chapter 3 – part two – Español (PDF)
Chapter 4 – Section 4(f) Analysis
Chapter 4 – Section 4(f) Analysis – English (PDF)
Chapter 4 – Section 4(f) Analysis – Español (PDF)
Chapter 5 – Section 6(f)
Chapter 5 – Section 6(f) – English (PDF)
Chapter 5 – Section 6(f) – Español (PDF)
Chapter 6 – Coordination
Chapter 6 – Coordination – English (PDF)
Chapter 6 – Coordination – Español (PDF)
Chapter 7 – Preparers
Chapter 7 – Preparers – English (PDF)
Chapter 7 – Preparers – Español (PDF)
Chapter 8 – Distribution
Chapter 8 – Distribution – English (PDF)
Chapter 8 – Distribution – Español (PDF)
Chapter 10 – Index
Appendices
Appendix 1A: Purpose and Need Chapter Supplemental Information
Appendix 2A: Alternatives Screening Report
Appendix 2B: Action Alt Design Figures
Appendix 3A: Property Impact Tables
Appendix 3B: Property Impact Figures
Appendix 3C: Environmental Justice Data Tables
Appendix 3D: Alternatives Operations Analysis Memo
Appendix 3E: Project of Air Quality Concern Evaluation
Appendix 3F: Noise Technical Report
Appendix 3G: Architectural Impacts
Appendix 3H: Cultural Resources Maps
Appendix 3I: Cultural Resources Correspondence
Appendix 3J: Water Quality Technical Report
Appendix 3K: Aquatic Resources Impacts
Appendix 3L: Biological Resources Evaluation Report
Appendix 3M: Aquatic Resources Delineation Report
Appendix 3N: Hot-spot Analysis
Appendix 4A: Figures for Section 4(f) Public Parks and Recreation Areas
Appendix 4B: Section 4(f) Correspondence
Appendix 6A: Public Involvement Materials for the Draft EIS September 2023
Appendix 9A: Reproductions of Comments on the Draft EIS and Response Matrix
Appendix 9B: Attachments to Emailed Comments on the Draft EIS
Design Resources
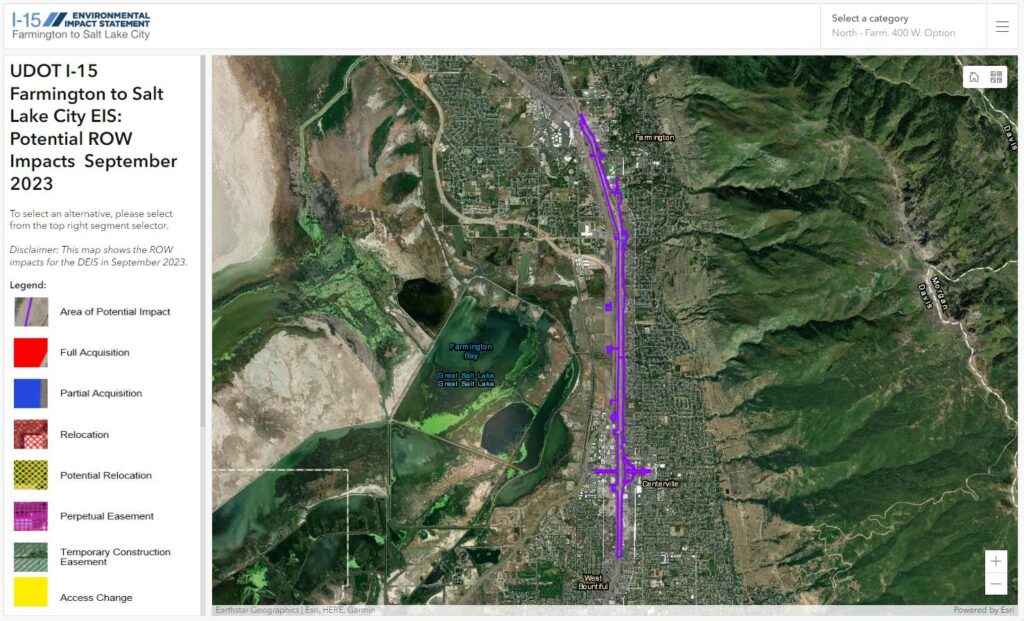
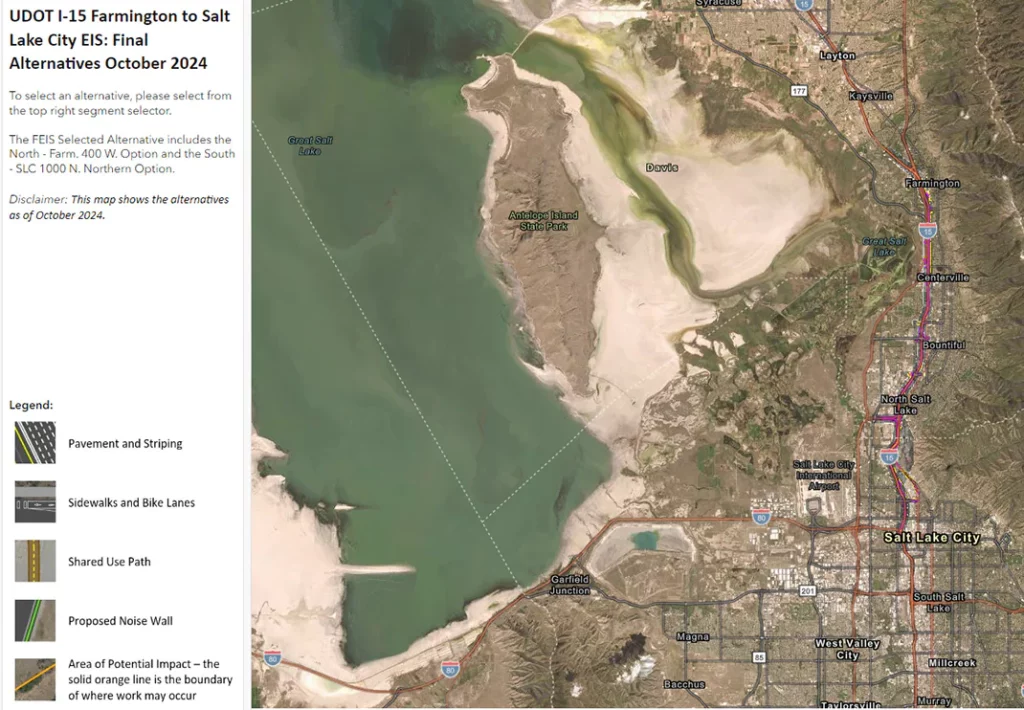
Property Impact Map
This map outlines the impacts to property as defined in the FEIS Report in Fall 2024. Zoom into any areas to see more detail.
Final EIS Phase Frequently Asked Questions
The following comment and question themes have been compiled during the I-15 Farmington to Salt Lake City Environmental Impact Statement (EIS), updated prior to the Final EIS release and ROD release.
Process Questions
Primary Response
- Based on the record of decision, our next step is to prepare for construction.
- This includes additional design work, coordination with local governments and other third parties such as utility companies, acquisition of necessary property, budget allocation, and identifying and hiring a project team to finalize and construct the project.
- We currently estimate that construction would begin as soon as 2027.
Primary Response
- Chapter 9 of the Final EIS provides responses to comments received on the Draft EIS. The Final EIS Summary Section S.6 describes changes made between the Draft EIS and Final EIS. Many of these changes were made based on comments received on the Draft EIS.
- We have read all comments from past comment periods and considered them as part of the overall analysis of transportation options in arriving at the final alternative.
Detailed Response
- Public comment is one factor in the overall decision-making process of an EIS. This process includes assessment of technical, regulatory, environmental and social factors and potential impacts, along with public comment. Given that public comment is one factor balanced among many other considerations, public comment is not a vote, meaning that if one alternative receives a lot of positive comments and another receives a lot of negative, other consideration may still suggest moving forward with an option less preferred as indicated by comments received.
Primary Response
- The Record of Decision is the final decision for the EIS process and documents UDOT’s selected alternative for the project.
- Consistent with federal law, UDOT has issued a combined Final EIS and Record of Decision and no additional formal public comment periods are required.
Detailed Response
- UDOT has assessed and responded to comments received on the Draft EIS in the Final Environmental Impact Statement (FEIS). The final selected alternative is documented in the Record of Decision (ROD) that is the final approval for a project to proceed.
Primary Response
- Funding for both the current Environmental Impact Statement and the potential construction of any improvements approved as part of the environmental study have been provided by the State of Utah.
Detailed Response
- Existing State funding is supporting the current Environmental Impact Statement (EIS) effort.
- $1.7 billion of state transportation funding has been allocated for future construction. This could fund construction for a portion of the preferred alternative. High-level estimates prepared during the environmental process indicate a total project cost of $3.7 billion.
- Future construction decisions, including how and when to construct certain portions of the project and if additional funding is available, will be made between now and construction.
I-15 Questions
Primary Response
- While the growing population of Utah and the aging pavement and bridges along I-15 in the study area require that we look at ways to improve mobility along the freeway itself, including adding capacity to meet the growing demand, we have put significant focus on a holistic approach to transportation within this corridor. That includes how best to get people where they’re going safely and easily, whether it be in a vehicle, on a bus or train, or on a bicycle or by foot. Widening I-15 is part of a comprehensive approach to meeting transportation demand through the year 2050 that includes added capacity to FrontRunner, additional bus service, local and regional roadway improvements and new facilities for those who walk and bike.
Detailed Response
- Our analysis of travel demand assumes that all projects in the current Regional Transportation Plan – including roadway, transit and bike/pedestrian trails – are successfully implemented in addition to any improvements to I-15. This includes double tracking FrontRunner.
- After all those other improvements were assumed, it was clear additional freeway capacity was needed. Our team assessed how many lanes it would take to not just improve conditions today, but to improve conditions in 2050. We looked at several different widening options, alongside what would happen if we added no capacity to I-15. The widening options included the following:
- Widening to 3-4 general purpose lanes + 3 High Occupancy Toll (HOT) lanes
- Widening to 5 general purpose lanes + 2 reversible lanes (presented during the Alternatives Phase Comment Period)
- Widening to 5 general purpose lanes + 1 HOT lane (presented during the Alternatives Phase Comment Period)
- Widening to 5 general purpose lanes + 2 HOT lanes
- Widening to 6 general purpose lanes + 1 HOT lane
- Only the 5 general purpose + 1 HOT lane option and the 5 general purpose lanes + 2 reversible lanes option were presented during the Alternatives Phase because these provided benefit in 2050 with less impact as compared to the other, wider options. At Level 2 screening, it was determined that the 5 general purpose lanes + 1 HOT lane concept would provide benefit while minimizing impacts.
- If no capacity is added to I-15, even with all the other transportation improvements successfully implemented, we project it would take more than an hour to travel through the study area. By comparison, by implementing the 5 general purpose + 1 HOT lane option, we project a travel time of 30 minutes. While this is still an increase in travel time over today, we feel this best balances travel improvement with impact to the surrounding community.
Primary Response
- As Utah grows, people will need many options to get around, including by vehicle, transit, bicycle and walking. To accommodate the population growth we expect by 2050, we will need to expand all travel options. Our models account for projected growth, including demand from more people and the additional trips that may be taken by car because there is capacity. We have planned to accommodate some – but not all – of the expected growth in demand for travel on I-15. To fully meet the expected demand for freeway travel it would require more lanes than UDOT understands the community would like to see.
Detailed Response
- Utah, the Wasatch Front and Intermountain West (Idaho, Montana, Colorado, and Nevada) are growing and are projected to continue to grow between now and 2050. The population of Utah in 1960 when this segment of I-15 was initially constructed was less than 900,000. In 2022 Utah’s population was approximately 3.3 million. The population in Utah is projected to be 5.0 million in 2050, with around 3.6 million people just in the Wasatch Front counties (Salt Lake, Davis, Weber, and Utah Counties).
- We consider both current and future demand in our transportation planning process. We need to accommodate our fastest-in-the-nation population growth, while keeping our system running smoothly and supporting the long-term plans of our cities, counties and metropolitan areas.
- We know that preparing for the future requires many transportation options, so we work closely with our partners – like UTA, local governments, regional planning agencies – to create more choices so people can get where they want in the way they want.
- We focus on identifying feasible improvements that provide the most value, because we’re committed to being good stewards of taxpayer funds and getting the most out of finite resources.
- It’s also important to note that I-15 is a regional facility serving national, regional, and local traffic. The interstate system fills an important role in the western U.S., not just Utah. In addition to moving people, it is estimated that the nation’s roadway system carries 71% of the freight we use as a society.
- UDOT uses the regional travel demand model that is jointly maintained by the Wasatch Front Regional Council (WFRC) and Mountainland Association of Government (MAG) to forecast future travel demand. This model has been reviewed by the Federal Highway Administration and Federal Transit Administration for use in transportation planning and is the best available model for this purpose. The travel demand model uses existing travel data and then predicts future travel demand based on projections for land use (from city, county, and region master plans), socioeconomic patterns such as population and employment growth, and the planned transportation networks (for all modes).
Transit/Travel Behavior Questions
Primary Response
- Traffic analysis shows that to meet the travel needs of all the people we expect to be in this area of Utah by 2050, all travel modes – roadways, transit, bike and pedestrian paths – will need to be expanded. Either transit or road expansion alone will not meet the need. Our study assumes that all other planned projects – roadway, transit and bike/pedestrian – are constructed when we evaluate what travel in the study area would look like without improvements to I-15. We then assess how improvements to I-15 and its adjacent roadways can help meet the transportation needs, not only for vehicles but also to better connect people to transit and bike and pedestrian opportunities.
Detailed Response
- There are currently funds programmed for both the FrontRunner Double Track (called FrontRunner Forward by UTA) and a potential I-15 project.
- Double tracking FrontRunner is a planned project on the 2050 RTP and is part of the I-15 EIS’s no-action scenario, which assumes all other roadway, transit, and active transportation projects in the 2050 RTP are constructed except the I-15 EIS project. The FrontRunner Double Track is currently in the environmental review and design process. The timing of construction has not been determined yet, but it is anticipated to begin construction shortly after the completion of the environmental and design process.
- UDOT is actively coordinating with UTA on the FrontRunner Forward/double track project. The I-15 alternative designs preserve space needed for UTA to construct the double track in areas where FrontRunner and I-15 are adjacent to one another (primarily in West Bountiful, Centerville and Farmington). UDOT, UTA, Woods Cross and Farmington are coordinating on ways to improve pedestrian, cyclist, and roadway connections to the Woods Cross and Farmington FrontRunner stations with the I-15 EIS project.
Primary Response
- Our study assumes all other projects – roadway, transit, bike and pedestrian – are completed and successful before assessing potential improvements to I-15. Even with all those other projects in place, I-15 remains a critical piece of mobility solutions now and in the coming decades. Further, the aging infrastructure of I-15 must be rebuilt for maintenance and safety reasons.
Detailed Response
- The 2050 RTP includes all transit projects identified by the Utah Transit Authority (UTA). The I-15 EIS’s no-action scenario assumes all other roadway, transit, and active transportation projects in the 2050 RTP are constructed except the I-15 EIS project. I-15 is one component of the region-wide transportation system. The WFRC 2050 RTP shows that additional capacity is needed on both I-15 and FrontRunner (as well as many other roadway and transit projects) to meet 2050 travel demand.
- A transit only alternative does not meet the project purpose. As stated in the project’s purpose and needs, in addition to mobility/capacity needs, the I-15 needs also include addressing aging infrastructure, improving access and providing safer pedestrian and bicyclist facilities.
Primary Response
- The traffic model we used to assess the needs along and around I-15 does account for expected changes in travel behavior between now and 2050. Even accounting for those changes and accounting for shifts to other modes of travel as those modes are improved and expanded, improvements to I-15 are still needed.
Detailed Response
- UDOT does not have jurisdiction on whether to allow or not allow development. The local cities and private property owners make decisions on local land use and development.
Impact Questions
Primary Response
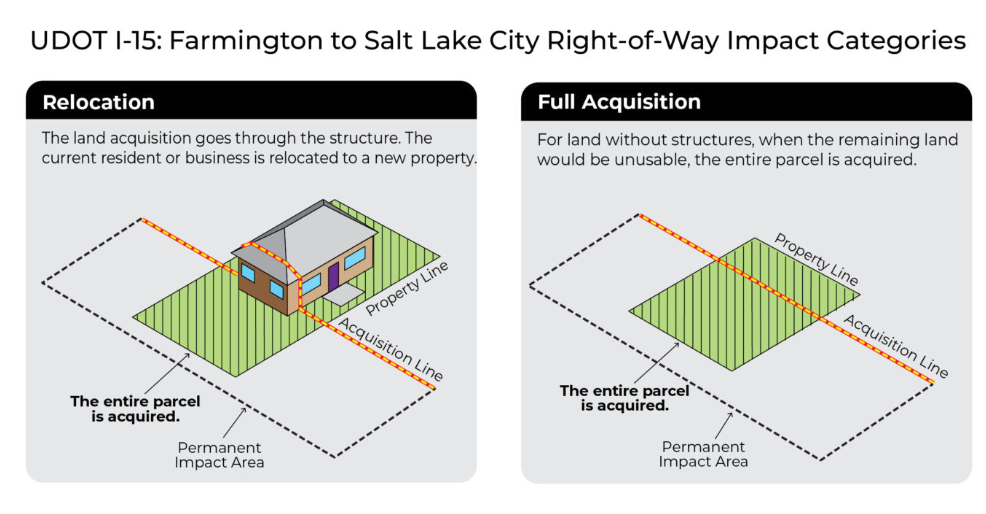
- In some cases, constructing the preferred alternative would result in impacts to a portion or all of a property. In those cases, UDOT must follow federal and state ROW procedures and processes (Acquisition Services | UDOT (utah.gov)).
Primary Response
- Section 3.3 of the Final Environmental Impact Statement (FEIS) includes information regarding potential property impacts. We invite you to review the information found on our study website and engage in the process to have questions answered and to provide comment to our team about any impacts.
Detailed Response
- In some areas, like Salt Lake City for example, there is some space between the northbound and southbound lanes of I-15 to add capacity toward the center, reducing needed width toward the outside of the current freeway footprint. As of the release of the FEIS, there are no required residential relocations in Salt Lake City.
- In other areas there is more available space on one side of the freeway or cross-street. Where that is the case, we have done our best to use that available space before impacting homes or businesses.
- In some cases, the necessary improvements have resulted in proposed impacts to a portion or all of a property. In those cases, UDOT must follow federal and state ROW procedures and processes (Acquisition Services | UDOT (utah.gov)).
Primary Response
- Generally, emissions from cars and trucks that contribute to our air quality challenges will continue to decrease even as we grow, thanks primarily to improvements in vehicle technology and cleaner fuels. Our study has assessed the anticipated emissions from the project alternatives (see Section 3.8 of the Final Environmental Impact Statement and Appendix 3N: Air Quality Technical Report: Hot-spot Analysis). The regional air quality effects from this project, along with all other planned transportation projects in the region, is assessed as part of the Regional Transportation Planning process.
Detailed Response
- Transportation is one source/sector that contributes to air quality issues in the Salt Lake Valley and includes vehicle emissions from personal vehicles, FrontRunner, buses, airplanes, and motorcycles. Other primary sources include industrial and commercial point sources, and area sources, which include emissions from residential and commercial development (furnaces, dry cleaners, restaurants, lawn mowers, etc.).
- Air quality impacts from the project have been analyzed in the EIS (see Section 3.8 and Appendix 3N: Air Quality Technical Report: Hot-spot Analysis) and follow FHWA and UDOT policies and procedures using approved air quality models. Generally, vehicle emission rates per mile are lower (better) at higher speeds/free-flowing traffic conditions compared to low-speeds/congested conditions.
- We are also aware of a study being conducted by the US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) on air quality on the west side of Salt Lake City. We have connected with those leading the study and are using learnings from that effort in our planning.
- The number of lanes on I-15 proposed with the I-15 EIS alternatives is consistent with the assumptions in the WFRC 2050 RTP. The WFRC 2050 RTP conducts a regional air quality conformity analysis, which takes into account anticipated emissions from all existing and planned 2050 major transportation facilities (Microsoft Word – AQ memo39_RTP_2019-2050_FINAL.docx (wfrc.org)).
- The air quality modeling analysis for the project documented in Appendix 3N: Air Quality Technical Report: Hot-spot Analysis shows that predicted pollutant concentrations from the project would not exceed national ambient air quality standards for any receptors in the project study area.
Primary Response
- Section 3.9 and Appendix 3F of the Final Environmental Impact Statement (FEIS) includes information regarding potential noise impacts and recommended mitigation measures (noise barriers). We invite you to review the information found on our study website and engage in the process to have questions answered and to provide comment to our team about any impacts.
Detailed Response
- The assessment of noise impacts and mitigation will follow the UDOT Noise Abatement Policy and procedures (Noise Walls | UDOT (utah.gov)).
Primary Response
- We understand that alternatives we are studying have potential to cause impacts to historically underserved populations. Further, we know I-15 is a barrier within communities. With this study we have identified ways to provide better connections across I-15 via vehicle, bicycle or walking and to better connect to transit options to improve conditions while also minimizing any impacts to specific communities as much as possible. See Section 3.4 of the FEIS for the Environmental Justice analysis for more information.
Detailed Response
- UDOT is aware of underserved communities and will try to minimize impacts from the project and provide new amenities/improvements to help mitigate current and past impacts related to I-15. A more detailed Environmental Justice (EJ) analysis that follows all current federal rules, regulations, and guidance for both public involvement and impacts assessment is found in Section 3.4 of the FEIS.
Primary Response
- UDOT acknowledges impacts of past decision-making on the west side of Salt Lake City. With this study, we have sought ways to not only minimize further transportation impacts to these communities, but also to provide better connections across I-15 via vehicles, bicycle or walking and to better connect to transit options, to enhance mobility for all people in this portion of the study area.
Detailed Response
- UDOT is aware of past actions and impacts, particularly in Salt Lake City (from I-15 and other actions unrelated to UDOT). UDOT has attempted to minimize impacts to the adjacent neighborhoods as much as possible during design while meeting the needs for the project. Consistent with its Quality of Life Framework and the purpose and need for the project, UDOT is proposing new connections and safer, more community-friendly access points and crossings and an upgraded Warm Springs interchange to try to take some truck traffic out of residential areas around 600 N. to help reduce the east-west divide and improve community connections.
- Proposed transportation improvements are meant to benefit all transportation users in the area, including those who use I-15, 600 North and 1000 North. A functional/less congested I-15 and I-15/600 North interchange that improves mobility is also a benefit to adjacent neighborhoods who use I-15 to access their neighborhoods.
Environmental Study Process
The study team is following the EIS process established by the National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA). This includes:
- Learning about issues, needs and potential solutions from the public and other stakeholders.
- Establishing a purpose and need for any proposed improvements.
- Developing a broad range of potential transportation solutions.
- Evaluating environmental impacts of those proposed solutions.
- Selecting an alternative that best meets the needs.
- Continuous public and stakeholder engagement.
NEPA Process Video (English)
NEPA Process Video (Español)
Quality of Life Framework
As the population in Utah continues to grow at a record pace, transportation planning and development play a key role in keeping Utah moving, facilitating a strong economy, and maintaining a high quality of life. As such this study will use the Quality of Life Framework outlined below to inform decision making including in developing the study Purpose and Need.

Contact the Study Team
For updates, join the Facebook group or get on our study email list.